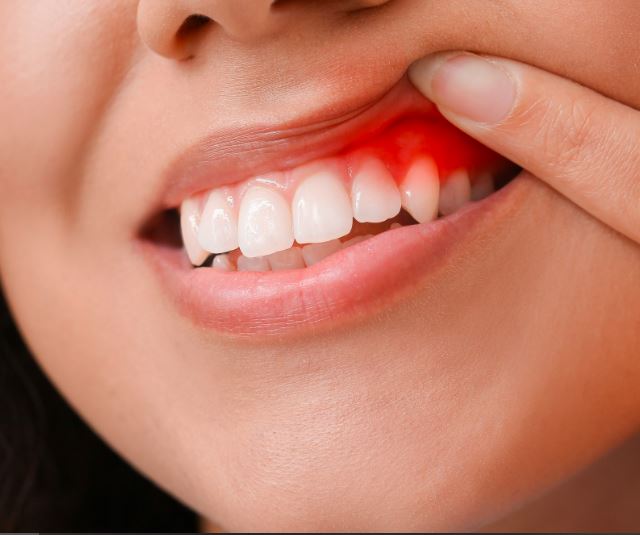
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a condition that affects the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth. It typically starts with the inflammation of the gums, known as gingivitis, and can progress to more severe stages if left untreated.
Gingivitis:
- Gingivitis is the initial stage of gum disease.
- It is characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing.
- Gingivitis is usually caused by the buildup of plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—on the teeth and gums.
Periodontitis:
- If gingivitis is not addressed, it can progress to periodontitis.
- Periodontitis involves the inflammation of the deeper supporting structures of the teeth, including the bone.
- Pockets may form between the teeth and gums, leading to the accumulation of more bacteria and plaque.
- Over time, the bone supporting the teeth can be damaged, potentially leading to tooth loss.
Common risk factors for gum disease include poor oral hygiene, smoking, diabetes, hormonal changes (such as pregnancy or menopause), certain medications, and genetic predisposition.
Preventing gum disease involves practicing good oral hygiene, including regular brushing, flossing, and professional dental cleanings. Early detection and intervention are crucial to managing gum disease effectively and preventing its progression to more severe stages. If you notice signs of gum disease, such as bleeding gums or persistent bad breath, it’s essential to consult with your dentist for proper evaluation and treatment.
How to Prevent and Treat Gum Disease
Preventing and treating gum disease involves a combination of good oral hygiene practices and professional dental care. Here are some tips:
Prevention:
- Brushing: Brush your teeth twice a day using fluoride toothpaste. Make sure to brush along the gumline and all surfaces of your teeth.
- Flossing: Floss daily to remove plaque and debris from between your teeth and below the gumline.
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Schedule regular dental check-ups and cleanings. Professional cleanings help remove plaque and tartar that regular brushing and flossing may miss.
- Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit sugary snacks and beverages, as they contribute to plaque formation.
- Avoid Smoking: Quit smoking or using tobacco products, as they increase the risk of gum disease.
- Limit Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to gum disease. Drink alcohol in moderation.
Treatment:
- Scaling and Root Planing: For early stages of gum disease, a deep cleaning procedure called scaling and root planing may be performed to remove plaque and tartar from below the gumline and smooth the root surfaces.
- Antibiotics: In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to control bacterial infection and inflammation.
- Laser Therapy: Advanced cases of gum disease may be treated with laser therapy to remove infected tissue and promote healing.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical procedures such as flap surgery or bone and tissue grafts may be necessary to restore gum health.
- Ongoing Maintenance: Following treatment, maintaining good oral hygiene and attending regular dental check-ups is crucial to prevent the recurrence of gum disease.
It’s important to consult with your dentist if you notice signs of gum disease, such as bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, or changes in gum appearance. Early intervention can help prevent the progression of gum disease to more severe stages.

Leave a Reply